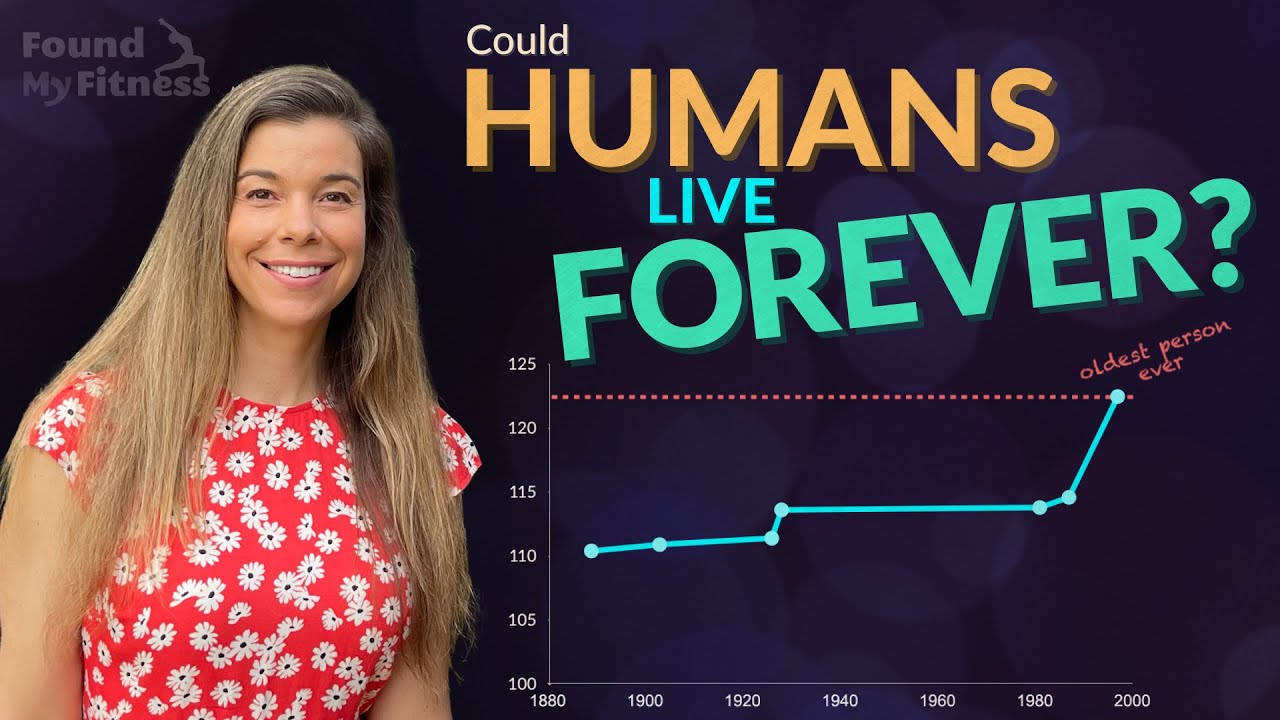
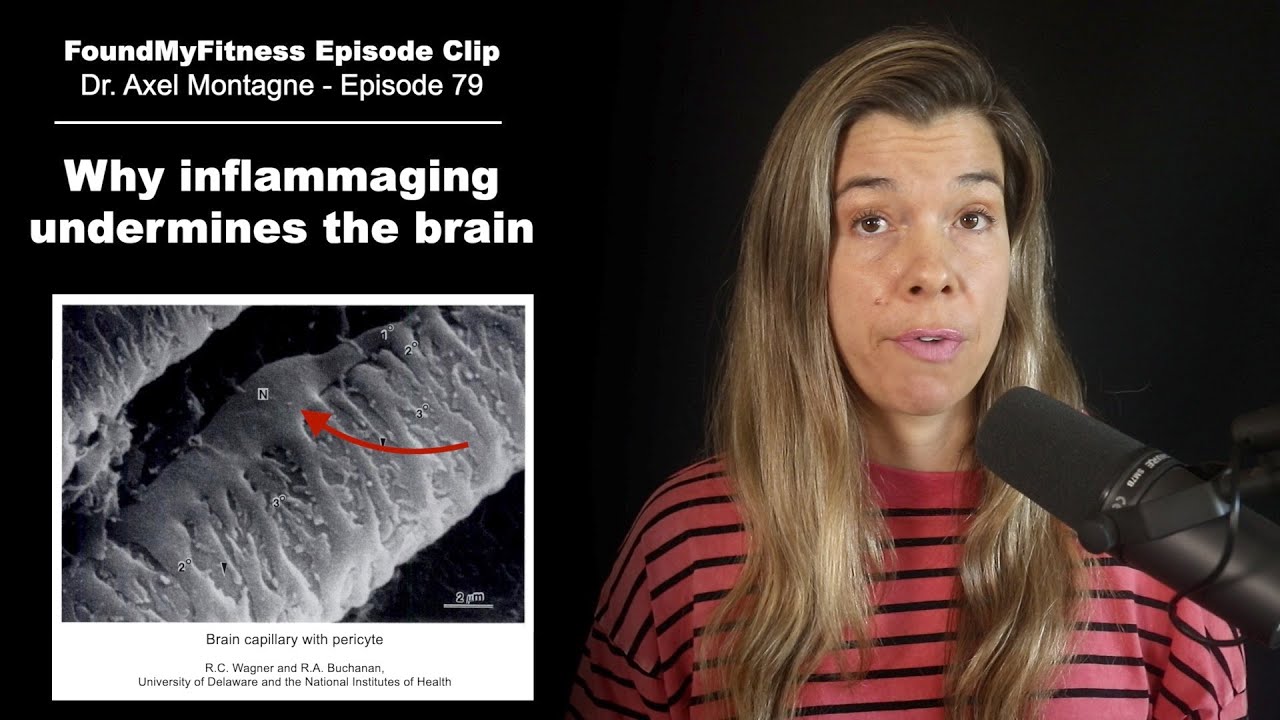
NMN supplementation reduced aging in mice (broad array of parameters) | David Sinclair
Get the full length version of this episode as a podcast.
This episode will make a great companion for a long drive.
The Omega-3 Supplementation Guide
A blueprint for choosing the right fish oil supplement — filled with specific recommendations, guidelines for interpreting testing data, and dosage protocols.
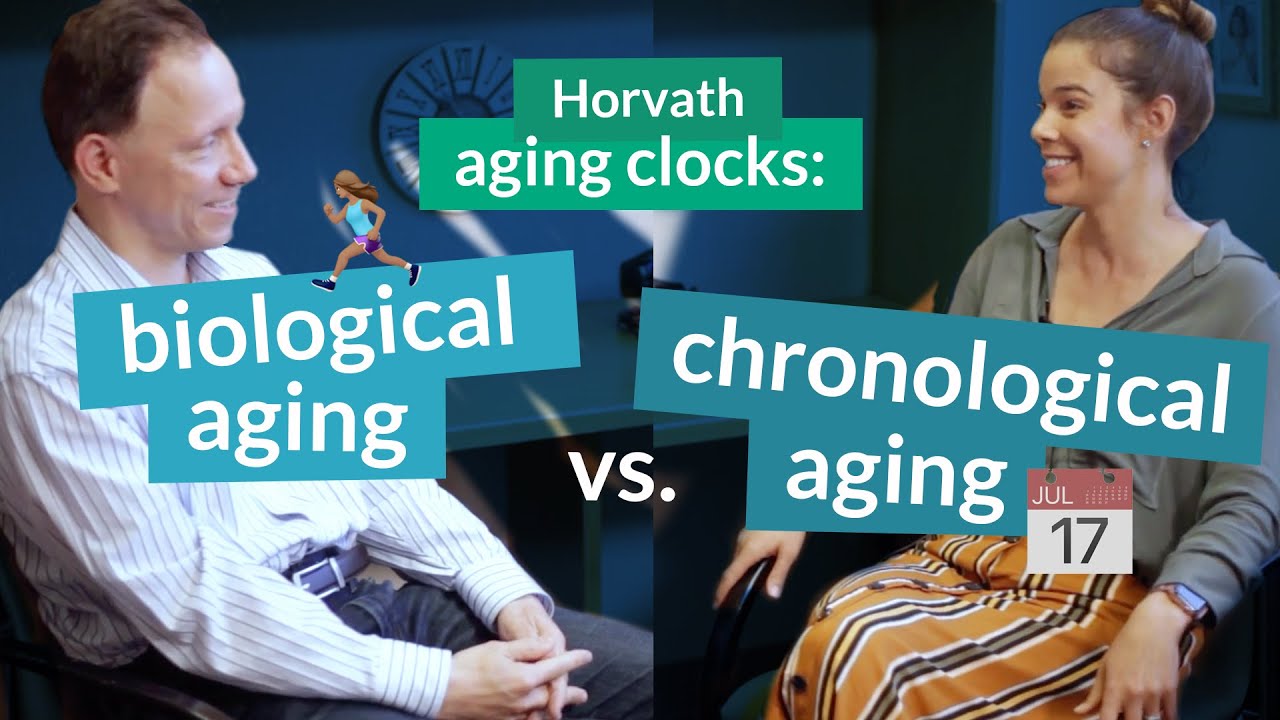
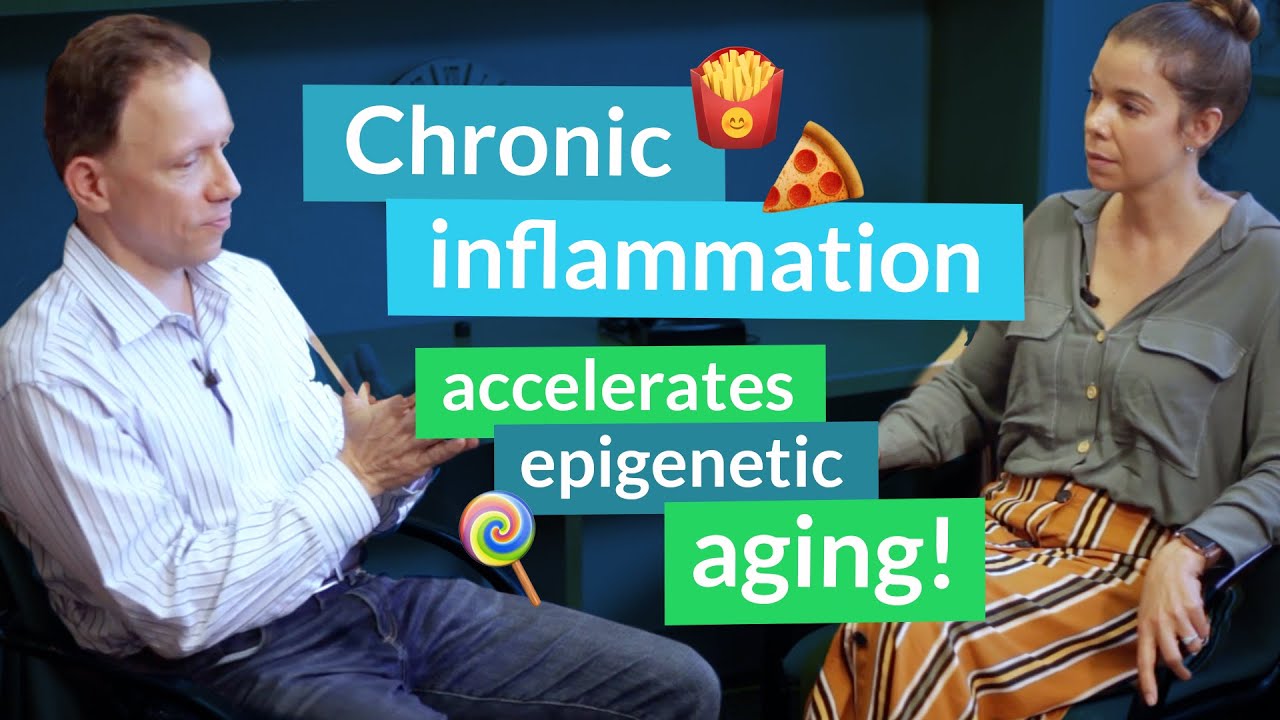
Previous studies on nicotinamide mononucleotide, an NAD+ precursor, demonstrated that the molecule is effective in increasing NAD+ levels across multiple tissues while improving the outcome of a variety of age-related diseases in rodents. Current research on rodents indicates that nicotinamide mononucleotide improves frailty and heart function. Although these studies are promising in terms of rodent health, the questions of whether they work in humans and at what dose remain unanswered. In this clip, Dr. David Sinclair discusses the current state of research on nicotinamide mononucleotide.
Rhonda: I was super excited. I think it was the 2016 "Cell" paper, you mentioned the group that published the NMN, basically, that was given to normal mice without any...
David: Yeah. Shin Imai's study.
Rhonda: Shin Imai's study. That's right. And basically, I think it was about 200 milligrams per day, like that dose, because I remember looking at the dose and going, "This is significantly lower than a nicotinamide riboside dose. And it seemed to delay tissue aging in multiple organs where, I mean, it was like... I don't know, did it extend lifespan?
David: He didn't take it long enough. He ran out of material. And in those days, NMN was hard to get and it was very expensive. It still is very expensive. We're still paying tens of thousands per kilo. But what he showed was that over a year of treatment, pretty much all the parameters of health in these mice were improved. And if those mice didn't live longer, I'd be surprised. But we have done an NMN lifespan in my lab and it's still ongoing and it's being crowdsource funded. So thank you for your donations. But it, already, it looks significantly different. The group that's on NMN in their water supply. And also, it improves frailty. In other words, they're less frail. Looks like it improves heart function as well. The dose, I can't exactly remember what we're using. It's probably around the 400, which is what's our standard dose, but don't quote me. But yeah, NMN and NR seem to do remarkable things to rodents. But like you say, like you brought up the challenges, A, does it work in humans? And B, if it does, what dose is necessary to get those effects?
Rhonda: Right.
Dietary supplements that purportedly increase cellular levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). Examples of potential NAD+ boosters include resveratrol (a plant-based dietary compound found in grapes), metformin (a type of diabetes medication), and nicotinamide mononucleotide (a derivative of niacin).
A coenzyme that is required for the production of energy in cells. NAD+ is synthesized from three major precursors: tryptophan, nicotinic acid (vitamin B3), and nicotinamide. It regulates the activity of several key enzymes including those involved in metabolism and repairing DNA damage. NAD+ levels rise during a fasted state. A group of enzymes called sirtuins, which are a type of histone deacetylase, use NAD+ to remove acetyl groups from proteins and are important mediators for the effects of fasting, caloric restriction, and the effects of the plant compound resveratrol, a so-called caloric restriction mimetic.
A precursor molecule for the biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme that participates in the production of cellular energy and repair. NMN helps maintain cellular levels of NAD+, thereby facilitating NAD+-dependent cellular activities, such as mitochondrial metabolism, regulation of sirtuins, and PARP activity. Animal studies have demonstrated that NMN administration is effective in increasing NAD+ levels across multiple tissues while improving the outcome of a variety of age-related diseases. Although NMN administration has proven to be safe and to effectively increase NAD+ levels in rodents, the safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation in humans remain unknown. NMN is available in supplement form and is present in various types of food, including broccoli, avocado, and beef. It is also an intermediate compound in the NAD+ salvage pathway, the recycling of nicotinamide into NAD+.
A precursor molecule for the biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme that participates in the production of cellular energy and repair. NMN helps maintain cellular levels of NAD+, thereby facilitating NAD+-dependent cellular activities, such as mitochondrial metabolism, regulation of sirtuins, and PARP activity. Animal studies have demonstrated that NMN administration is effective in increasing NAD+ levels across multiple tissues while improving the outcome of a variety of age-related diseases. Although NMN administration has proven to be safe and to effectively increase NAD+ levels in rodents, the safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation in humans remain unknown. NMN is available in supplement form and is present in various types of food, including broccoli, avocado, and beef. It is also an intermediate compound in the NAD+ salvage pathway, the recycling of nicotinamide into NAD+.
Member only extras:
Learn more about the advantages of a premium membership by clicking below.
Supporting our work
If you enjoy the fruits of
 , you can participate in helping us to keep improving it. Creating a premium subscription does just that! Plus, we throw in occasional member perks and, more importantly, churn out the best possible content without concerning ourselves with the wishes of any dark overlords.
, you can participate in helping us to keep improving it. Creating a premium subscription does just that! Plus, we throw in occasional member perks and, more importantly, churn out the best possible content without concerning ourselves with the wishes of any dark overlords.