Nicotinamide riboside for prevention of hearing loss and the importance of NAD+ for mitochondria | Eric Verdin
Get the full length version of this episode as a podcast.
This episode will make a great companion for a long drive.
The Omega-3 Supplementation Guide
A blueprint for choosing the right fish oil supplement — filled with specific recommendations, guidelines for interpreting testing data, and dosage protocols.
Mitochondria play an essential role in aging. By studying aging pathways, scientists have recognized that maintaining efficient mitochondria is a fundamental approach to staying young. In animal studies, the mitochondrial enzyme nicotinamide riboside, when provided as a supplement, protected the animals against age- or noise-induced hearing loss. Other studies have explored how NAD supplementation affects global mitochondrial function and DNA damage. In this clip, Dr. Eric Verdin discusses several ways in which NAD+ supplementation can benefit mitochondrial health and play a protective role against aging.
This transcript is reserved for members.
FoundMyFitness Members get access to exclusive content not available anywhere else, including a transcript of this episode.
You wouldn't believe how cool being a premium member of the world's best cross-disciplinary science-focused website and podcast really is.
Acetyl coenzyme A is a molecule that was first discovered to transfer acetyl groups to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for energy production. Now it is known to be involved in many different pathways including fatty acid metabolism, steroid synthesis, acetylcholine synthesis, acetylation, and melatonin synthesis.
An intracellular degradation system involved in the disassembly and recycling of unnecessary or dysfunctional cellular components. Autophagy participates in cell death, a process known as autophagic dell death. Prolonged fasting is a robust initiator of autophagy and may help protect against cancer and even aging by reducing the burden of abnormal cells.
The relationship between autophagy and cancer is complex, however. Autophagy may prevent the survival of pre-malignant cells, but can also be hijacked as a malignant adaptation by cancer, providing a useful means to scavenge resources needed for further growth.
A chemical produced in the liver via the breakdown of fatty acids. Beta-hydroxybutyrate is a type of ketone body. It can be used to produce energy inside the mitochondria and acts as a signaling molecule that alters gene expression by inhibiting a class of enzymes known as histone deacetylases.
A major contributing factor to aging, cellular senescence, and the development of cancer. Byproducts of both mitochondrial energy production and immune activity are major sources of DNA damage. Additionally, environmental stressors can increase this base level of damage. DNA damage can be mitigated by cellular repair processes; however, the effectiveness of these processes may be influenced by the availability of dietary minerals, such as magnesium, and other dietary components, which are needed for proper function of repair enzymes.
Any of a group of complex proteins or conjugated proteins that are produced by living cells and act as catalyst in specific biochemical reactions.
A series of enzyme-dependent reactions that breaks down glucose. Glycolysis converts glucose into pyruvate, releasing energy and producing ATP and NADH. In humans, glycolysis occurs in the cytosol and does not require oxygen.
The chief protein components of chromatin found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes acting as spools around which DNA winds, and playing a role in gene regulation.
A diet that causes the body to oxidize fat to produce ketones for energy. A ketogenic diet is low in carbohydrates and high in proteins and fats. For many years, the ketogenic diet has been used in the clinical setting to reduce seizures in children. It is currently being investigated for the treatment of traumatic brain injury, Alzheimer's disease, weight loss, and cancer.
Tiny organelles inside cells that produce energy in the presence of oxygen. Mitochondria are referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell" because of their role in the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Mitochondria are continuously undergoing a process of self-renewal known as mitophagy in order to repair damage that occurs during their energy-generating activities.
The process by which new mitochondria are made inside cells. Many factors can activate mitochondrial biogenesis including exercise, cold shock, heat shock, fasting, and ketones. Mitochondrial biogenesis is regulated by the transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, or PGC-1α.
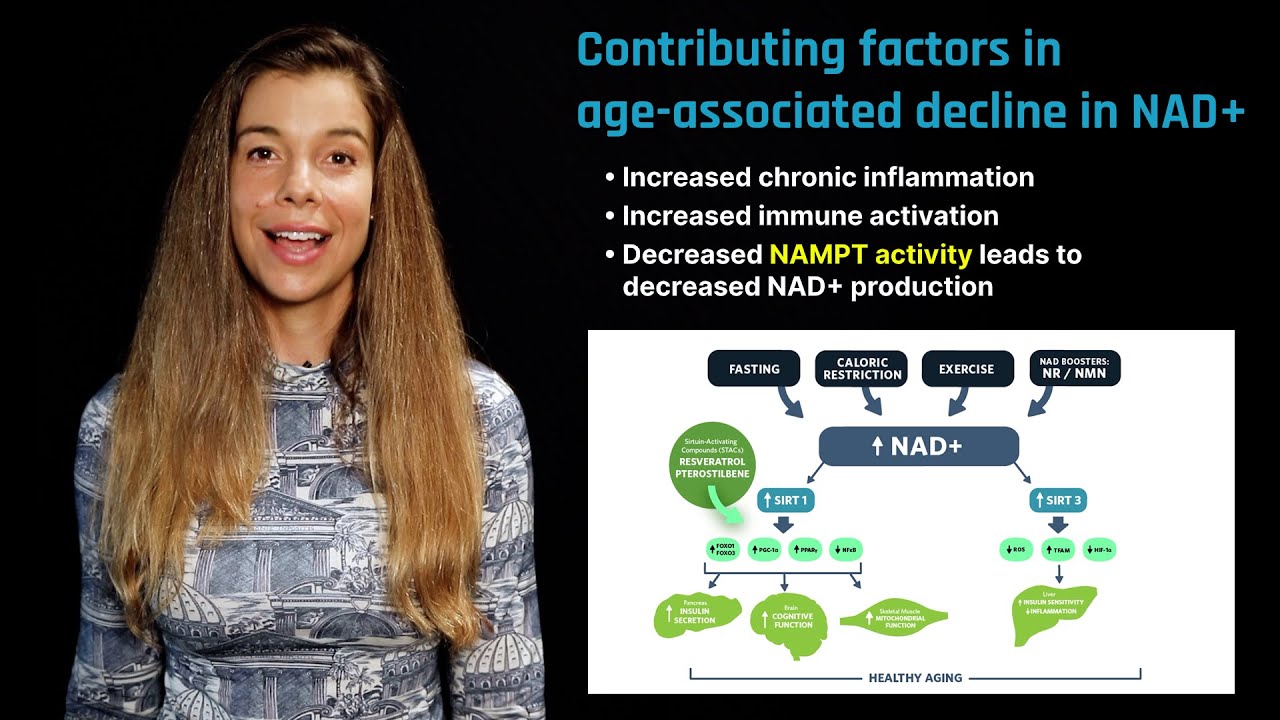
A coenzyme that is required for the production of energy in cells. NAD+ is synthesized from three major precursors: tryptophan, nicotinic acid (vitamin B3), and nicotinamide. It regulates the activity of several key enzymes including those involved in metabolism and repairing DNA damage. NAD+ levels rise during a fasted state. A group of enzymes called sirtuins, which are a type of histone deacetylase, use NAD+ to remove acetyl groups from proteins and are important mediators for the effects of fasting, caloric restriction, and the effects of the plant compound resveratrol, a so-called caloric restriction mimetic.
A precursor molecule for the biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme that participates in the production of cellular energy and repair. NMN helps maintain cellular levels of NAD+, thereby facilitating NAD+-dependent cellular activities, such as mitochondrial metabolism, regulation of sirtuins, and PARP activity. Animal studies have demonstrated that NMN administration is effective in increasing NAD+ levels across multiple tissues while improving the outcome of a variety of age-related diseases. Although NMN administration has proven to be safe and to effectively increase NAD+ levels in rodents, the safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation in humans remain unknown. NMN is available in supplement form and is present in various types of food, including broccoli, avocado, and beef. It is also an intermediate compound in the NAD+ salvage pathway, the recycling of nicotinamide into NAD+.
The process of generating energy that occurs when mitochondria couple oxygen with electrons that have been derived from different food sources including glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids.
A molecule that allows cells to perceive and correctly respond to their microenvironment, which enables normal cellular function, tissue repair, immunity, cognition, and more. Hormones and neurotransmitters are examples of signaling molecules. There are many types of signaling molecules, however, including cAMP, nitric oxide, estrogen, norepinephrine, and even reactive oxygen species (ROS).
A class of enzymes that influence that influence aging and longevity through multiple molecular pathways. Sirtuins regulate a variety of metabolic processes, including release of insulin, mobilization of lipids, response to stress, and modulation of lifespan. They also influence circadian clocks and mitochondrial biogenesis. Sirtuins are activated when NAD+ levels rise. The dependence of sirtuins on NAD+ links their enzymatic activity directly to the energy status of the cell via the cellular NAD+:NADH ratio, the absolute levels of NAD+, NADH or nicotinamide or a combination of these variables. There are seven known sirtuins, designated as Sirt1 to Sirt7.
A cell that has the potential to develop into different types of cells in the body. Stem cells are undifferentiated, so they cannot do specific functions in the body. Instead, they have the potential to become specialized cells, such as muscle cells, blood cells, and brain cells. As such, they serve as a repair system for the body. Stem cells can divide and renew themselves over a long time. In 2006, scientists reverted somatic cells into stem cells by introducing Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and cMyc (OSKM), known as Yamanaka factors.[1]
Member only extras:
Learn more about the advantages of a premium membership by clicking below.
Get email updates with the latest curated healthspan research
Support our work

Every other week premium members receive a special edition newsletter that summarizes all of the latest healthspan research.
Aging News
- Vitamin D increases muscle strength and mass without altering body weight in mice.
- Any Level of Physical Activity Tied to Better Later-Life Memory
- Allulose Attenuated Age-Associated Sarcopenia via Regulating IGF-1 and Myostatin in Aged Mice
- Exercise increases activity of anti-aging sirtuin enzymes in older adults with obesity.
- Blood levels of sirtuin enzymes decline with Alzheimer's disease progression, making them a potential biomarker.













































WE need some more discussion about NAD and its effect on Cancer cells. 10 years ago I had stage 4 Lymphoma, after chemo it went silent, now has re-appeared. The coincidence is I started taking NAD 6 months ago. I have stopped after seeing some rare papers on how NAD can speed up growth of cancer cells.