Can you get enough omega-3 from a vegan diet? | Rich Roll
Get the full length version of this episode as a podcast.
This episode will make a great companion for a long drive.
The Omega-3 Supplementation Guide
A blueprint for choosing the right fish oil supplement — filled with specific recommendations, guidelines for interpreting testing data, and dosage protocols.
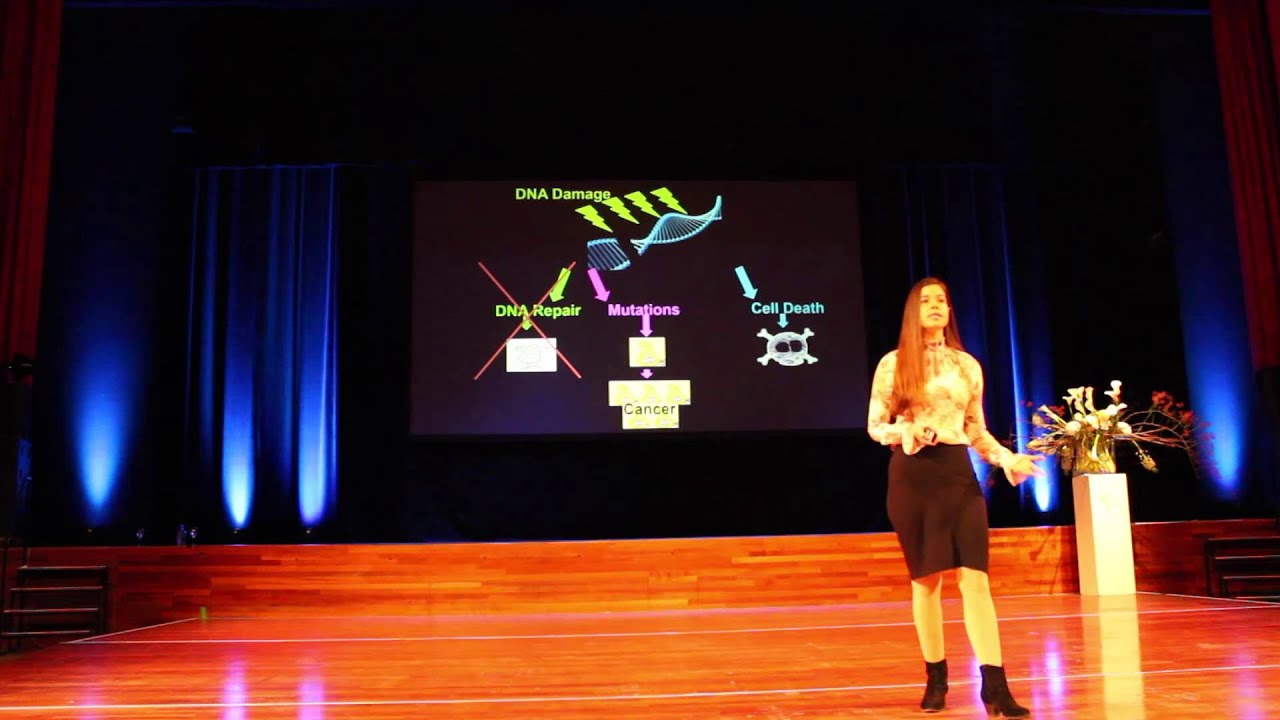
Obtaining adequate omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for human health, can be challenging for people on a vegan diet. Omega-3 fatty acids include alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is found mainly in plant oils such as flaxseed, soybean, and canola. DHA and EPA are found in fish and other seafood. The human body can convert some ALA into EPA and then to DHA, but the efficiency of the process varies between individuals. In this clip, Rich Roll and Dr. Rhonda Patrick discuss how those on a vegan diet can determine whether they are getting enough omega-3 fatty acids.
This transcript is reserved for members.
FoundMyFitness Members get access to exclusive content not available anywhere else, including a transcript of this episode.
You wouldn't believe how cool being a premium member of the world's best cross-disciplinary science-focused website and podcast really is.
An omega-3 fatty acid found mostly in plants. ALA can be converted into the omega-3 fatty acids EPA or DHA, but this conversion process is very inefficient in humans. When ALA is not converted to EPA or DHA, it remains inactive and is simply stored or used as energy, like other fats. Some evidence suggests an association between a diet rich in ALA and reduced risk of heart disease. Dietary sources of ALA include kale, spinach, soybeans, walnuts, seeds, and plant-based oils.
An omega-3 fatty acid found in the human brain and the meat of fatty fish. DHA plays a key role in the development of eye and nerve tissues, and is essential for normal brain function in humans. DHA may also reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease1 and cardiovascular disease, and may be useful in treating certain inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Dietary sources of DHA include krill oil and the meat and roe of salmon, flying fish, and pollock. [1] Patrick, Rhonda P. "Role of phosphatidylcholine-DHA in preventing APOE4-associated Alzheimer’s disease." The FASEB Journal (2018): fj-201801412R.
An omega-3 fatty acid found in the meat of fatty fish. EPA reduces inflammation in the body and helps counter oxidative stress in cells. It is crucial for modulating behavior and mood and has demonstrated beneficial effects in managing anxiety and depression. EPA may reduce risk of developing certain chronic diseases such as cancer or cardiovascular disease. Dietary sources of EPA include herring, salmon, eel, shrimp and sturgeon.
Get email updates with the latest curated healthspan research
Support our work

Every other week premium members receive a special edition newsletter that summarizes all of the latest healthspan research.
Omega-3 News
- Omega-3s protect the heart and muscles against damage incurred during endurance running.
- BDNF emerges as a critical marker of omega-3 fatty acid levels in the brain.
- Study shows people with a high omega-3 DHA level in their blood are at 49% lower risk of Alzheimer’s
- High-dose 2.4g EPA/DHA omega-3 in third trimester of pregnancy decreased the risk of wheeze & asthma during first 5 years of child's life by 54%
- Eating fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids reduces risk of asthma in some children.