How intermittent fasting enhances the parasympathetic nervous system | Dr. Mark Mattson
Get the full length version of this episode as a podcast.
This episode will make a great companion for a long drive.
The BDNF Protocol Guide
An essential checklist for cognitive longevity — filled with specific exercise, heat stress, and omega-3 protocols for boosting BDNF. Enter your email, and we'll deliver it straight to your inbox.
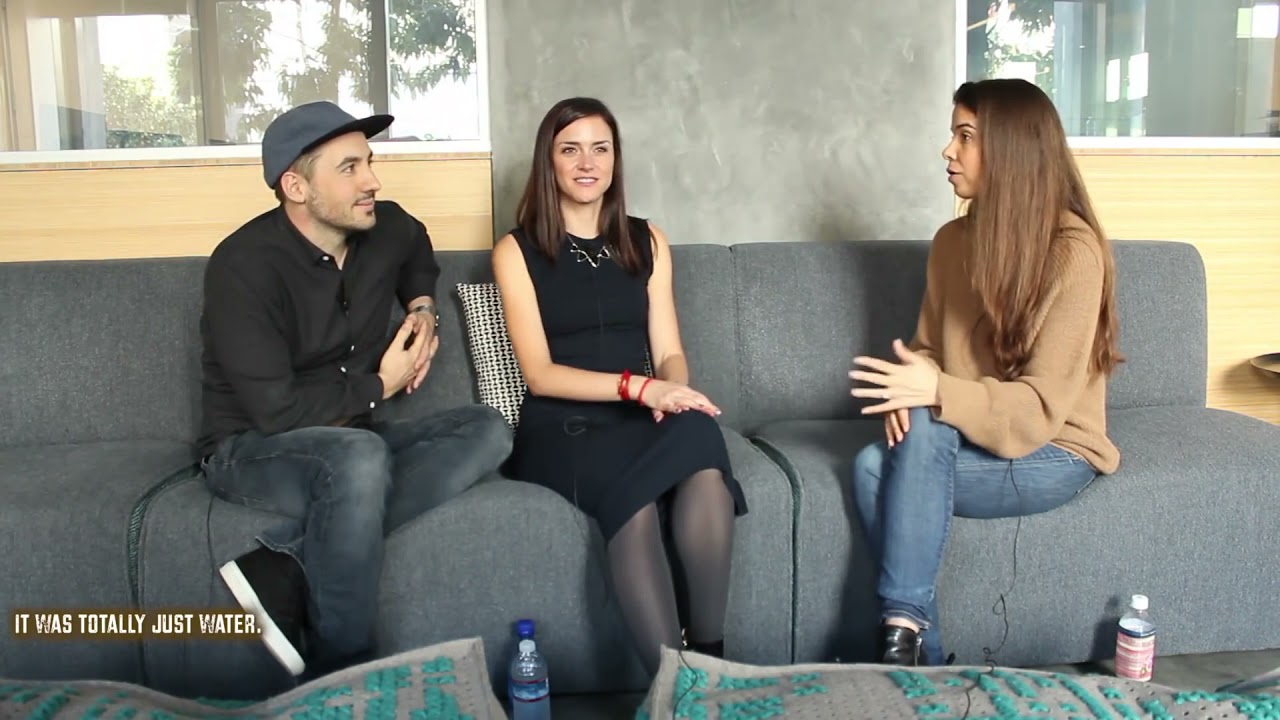
Previous research in animals shows that caloric restriction reduces resting heart rate and blood pressure, improving cardiovascular health. Aerobic exercise training also reduces resting heart rate and blood pressure, while increasing heart rate variability, a measure of variation in time between heart beats. Higher heart rate variability indicates adaptation to stress (i.e, exercise training) by the parasympathetic nervous system. Over time, exercise enhances the parasympathetic nerves that innervate the heart, slowing heart rate, and improving health. In this clip, Dr. Mark Mattson explains the importance of stressing the cardiovascular system with behaviors such as exercise and fasting to maximize health.
This transcript is reserved for members.
FoundMyFitness Members get access to exclusive content not available anywhere else, including a transcript of this episode.
You wouldn't believe how cool being a premium member of the world's best cross-disciplinary science-focused website and podcast really is.
The physiological phenomenon of variation in the time interval between heartbeats. It is measured by the variation in the beat-to-beat interval. Decreased parasympathetic nervous system activity or increased sympathetic activity will result in reduced HRV. Reduced HRV has been shown to be a predictor of mortality after myocardial infarction, and a range of other outcomes/conditions may also be associated.[1]
A broad term that describes periods of voluntary abstention from food and (non-water) drinks, lasting several hours to days. Depending on the length of the fasting period and a variety of other factors, intermittent fasting may promote certain beneficial metabolic processes, such as the increased production of ketones due to the use of stored fat as an energy source. The phrase “intermittent fasting” may refer to any of the following:
- Time-restricted eating
- Alternate-day fasting
- Periodic fasting (multi-day)
One of the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system (the other being the sympathetic nervous system). The parasympathetic nervous system's primary function is to control homeostasis and the body at rest. It conserves energy as it slows the heart rate, increases gut motility and hormonal activity, and relaxes sphincter muscles in the gastrointestinal tract.
Member only extras:
Learn more about the advantages of a premium membership by clicking below.
Attend Monthly Q&As with Rhonda
Support our work

The FoundMyFitness Q&A happens monthly for premium members. Attend live or listen in our exclusive member-only podcast The Aliquot.
Fasting News
- A fasting-mimicking diet improved effectiveness and reduced toxicity of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients.
- Exercise mitigates muscle mass losses during severe energy deficit by inhibiting the induction of autophagy.
- Time-restricted eating, a ketogenic diet, and exercise improved cognitive function and markers of metabolism in a woman with ApoE4 and Alzheimer's .
- A clinical trial found a fasting-mimicking diet decreased biomarkers of inflammation in humans. In mice, it reversed pathologies linked to Crohn's.
- Intermittent fasting could improve obese women's health