Reduction of inflammation from sulforaphane supplementation as a treatment for depression | Jed Fahey
Enter your email to get our 15-page guide to sprouting broccoli and learn about the science of chemoprotective compount sulforaphane.
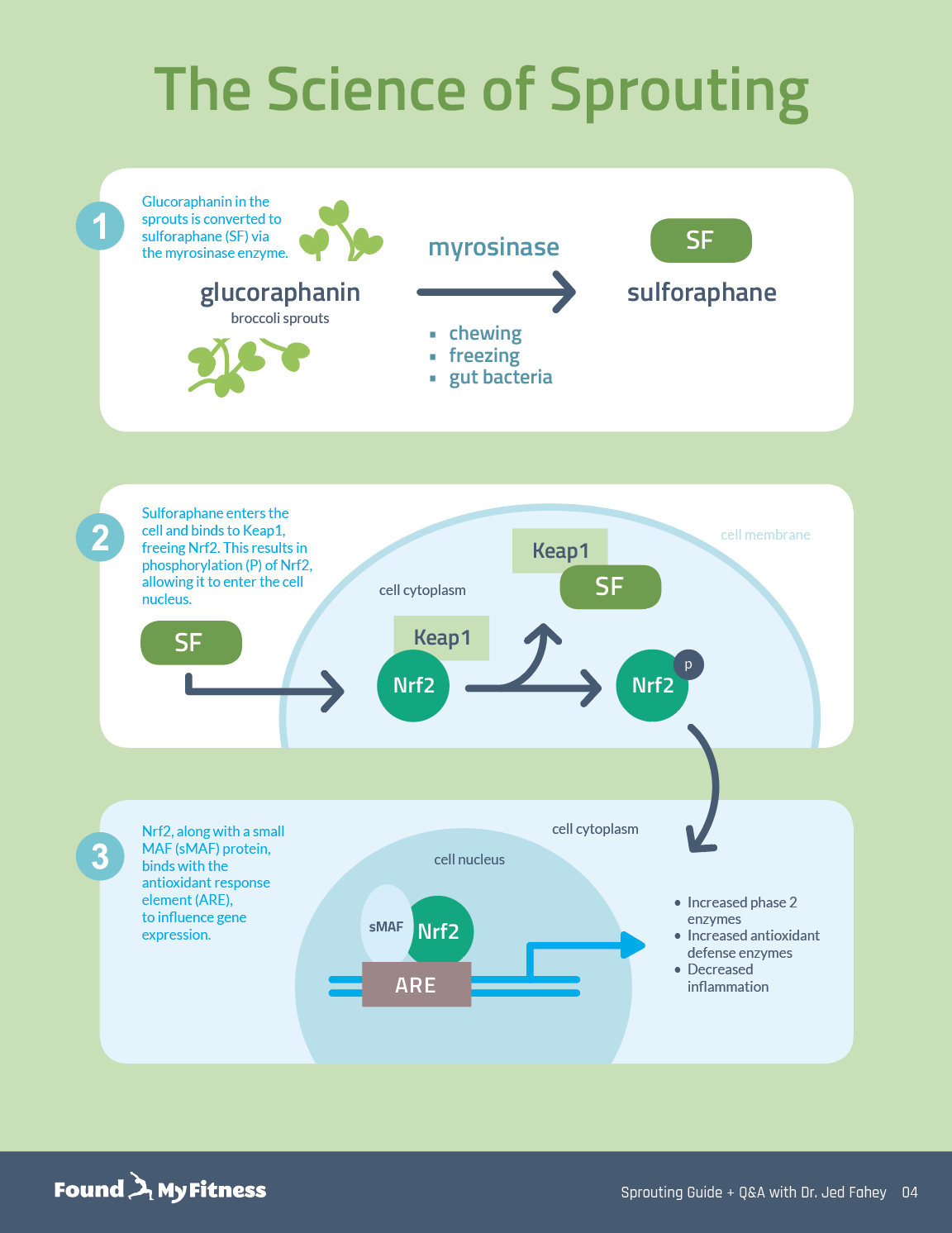
Broccoli sprouts are concentrated sources of sulforaphane, a type of isothiocyanate. Damaging broccoli sprouts – when chewing, chopping, or freezing – triggers an enzymatic reaction in the tiny plants that produces sulforaphane.
Get the full length version of this episode as a podcast.
This episode will make a great companion for a long drive.
Inflammation is a critical element of the body’s immune response. Chronic inflammation, which occurs on the cellular level in response to toxins or other stressors, plays a key role in the development of many diseases, including depression. Findings from rodent studies suggest that sulforaphane, the isothiocyanate compound derived from broccoli sprouts, may be beneficial in ameliorating the inflammation that fuels the condition. In this clip, Dr. Jed Fahey discusses the potential therapeutic benefit of sulforaphane in treating depression.
Rhonda: There's definitely a common denominator with oxidative stress and inflammation in both autism and schizophrenia, but also in depression. And this is another brain dysfunction, I guess, if you want to call it that, but inflammation has been shown now to play, actually, a major causal role in depression. And there's been some animals studies that you may have seen where the sulforaphane, broccoli sprout extract in sulforaphane has shown to be even as good as fluoxetine, which is Prozac, in alleviating, like, all these different methods of stress they have to make an animal depressed, and then they give it Prozac or broccoli sprout extract and it works just as well, which is extremely interesting.
Jed: I totally agree. We won't talk about the way those experiments are done here because I think they can be sort of...
Rhonda: Inhumane? Some of them? Some of them.
Jed: They're distressing to hear about, yeah. But needless to say, it's better to do them on mice than on people. Yes. In fact, just last week, I was at the Stanley Medical Research Institute, its annual meeting in Baltimore and there was a lot of talk about inflammation and depression. They're focusing on bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. And in fact, they funded the study at Sheppard Pratt that's just starting, as I say. So, yeah, I mean, there is so many conditions that we hope may respond even if only partially, and the fact that it can be a dietary approach is, I think...
Rhonda: Wouldn't that be cool?
Jed: That would be...
Rhonda: I mean, if people could, instead of getting on something with side effects possibly takes broccoli sprouts or some sort of broccoli sprout extract or supplement that's out there that's really effective, that would be so...because it's just, it's so good for you. The sulforaphane, the broccoli sprouts are so good for you. So I just would be really excited to see that happen.
A developmental disorder characterized by impaired social interaction, behavioral problems, and poor communication. Autism typically manifests in early childhood and is slightly more common among boys than girls. In clinical trials, sulforaphane, a compound derived from broccoli and broccoli sprouts, reduces the characteristic behaviors associated with autism.
A mood disorder characterized by profound sadness, fatigue, altered sleep and appetite, as well as feelings of guilt or low self-worth. Depression is often accompanied by perturbations in metabolic, hormonal, and immune function. A critical element in the pathophysiology of depression is inflammation. As a result, elevated biomarkers of inflammation, including the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, are commonly observed in depressed people. Although selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and cognitive behavioral therapy typically form the first line of treatment for people who have depression, several non-pharmacological adjunct therapies have demonstrated effectiveness in modulating depressive symptoms, including exercise, dietary modification (especially interventions that capitalize on circadian rhythms), meditation, sauna use, and light therapy, among others.
A critical element of the body’s immune response. Inflammation occurs when the body is exposed to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. It is a protective response that involves immune cells, cell-signaling proteins, and pro-inflammatory factors. Acute inflammation occurs after minor injuries or infections and is characterized by local redness, swelling, or fever. Chronic inflammation occurs on the cellular level in response to toxins or other stressors and is often “invisible.” It plays a key role in the development of many chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
A result of oxidative metabolism, which causes damage to DNA, lipids, proteins, mitochondria, and the cell. Oxidative stress occurs through the process of oxidative phosphorylation (the generation of energy) in mitochondria. It can also result from the generation of hypochlorite during immune activation.
A mental disorder characterized by abnormal social behavior and failure to understand what is real. Common symptoms include false beliefs, unclear or confused thinking, hearing voices that others do not, reduced social engagement and emotional expression, and a lack of motivation. People with schizophrenia often have additional mental health problems such as anxiety disorders, major depressive illness, or substance use disorders.
An isothiocyanate compound derived from cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and mustard. Sulforaphane is produced when the plant is damaged when attacked by insects or eaten by humans. It activates cytoprotective mechanisms within cells in a hormetic-type response. Sulforaphane has demonstrated beneficial effects against several chronic health conditions, including autism, cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and others.
Attend Monthly Q&As with Rhonda
Support our work

The FoundMyFitness Q&A happens monthly for premium members. Attend live or listen in our exclusive member-only podcast The Aliquot.
Sulforaphane News
- Sulforaphane extends lifespan and healthspan in worms via insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling.
- Paul Saladino, MD explains how we may have overstated the health benefits of plants and especially sulforaphane
- NRF2 much of a good thing (December 2017)
- A pilot trial finds sulforaphane treatment increased glutathione levels in the blood & hippocampus region of the brain in healthy people.
- A new study found sulforaphane (found in broccoli sprouts) improved behavior & social responsiveness in children with autism.





































































